Hurghada Red Sea Egypt in 2026 is one of the most dazzling and dyna...

Famous Simbolos Egipcios Significados are among the most significant aspects that reflect the culture of the pharaohs. These symbols were not merely drawings on walls but carried deep meanings and spiritual and religious connotations that expressed concepts of life, death, the cosmic order, and immortality.
These symbols embody the artistic creativity and intellectual depth of the ancient Egyptians, and they were associated with the most prominent gods and kings. For instance, the Eye of Horus, also known as the “udjat,” was considered a symbol of protection and power, while the Ankh symbol represented immortality and prosperity.
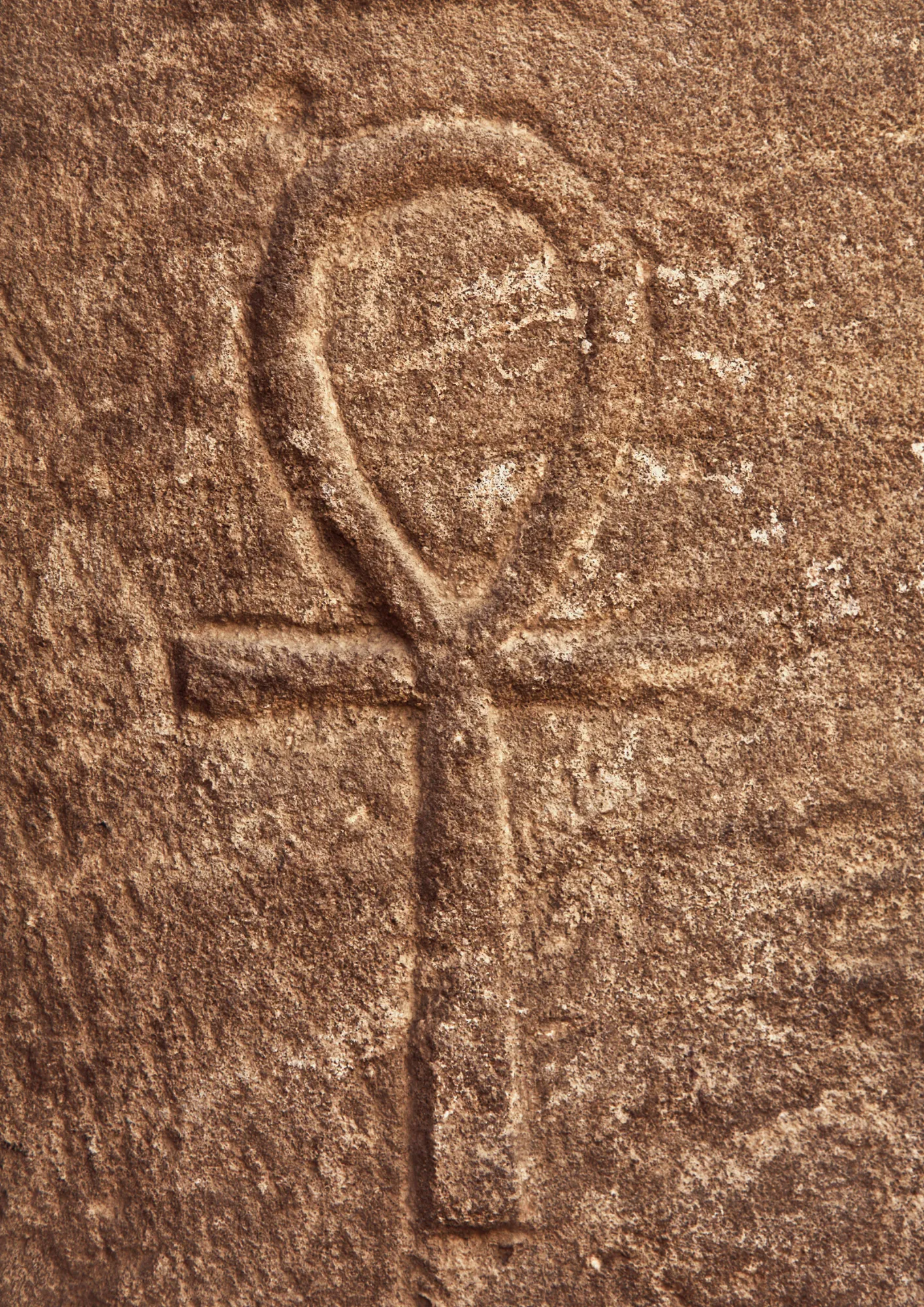
The Ankh, known as the key of life or the key of the Nile, is a significant symbol of eternal life in the culture of the ancient Egyptians. It was widely used by the pharaohs as a representation of life after death, as they believed it granted them the power for eternal life in the afterlife. For this reason, it is considered one of the famous Simbolos Egipcios Significados.
This symbol was carried by divine forces as well as the pharaohs, highlighting its high spiritual significance. The Ankh is an essential part of the religious and philosophical beliefs that dominated that era, symbolizing immortality and prosperity, surrounded by the mysteries and myths of ancient Egyptian civilization.
The Ankh frequently appears in tomb paintings of ancient Egypt, often used in depictions of the deceased being resurrected from the dead. The ancient Egyptians crafted decorative mirrors from metals in the shape of the Ankh, reflecting their religious view.
They also wore the Ankh as an amulet for protection, either alone or with two other charms symbolizing strength and health. They even placed metal models of the Ankh on tombs, plated with gold or copper, symbolizing the sun and reinforcing their belief in eternal life.
The Ankh is a significant symbol that reflects the close relationship between culture and nature in ancient Egypt. It is often associated with the concept of life and birth due to its resemblance to the womb. Some experts suggest that the twisted shape of the key, which takes an oval form and contains two opposing points, highlights the balance between the feminine and masculine, emphasizing the vital foundations that sustain life on Earth.
The symbol is also thought to represent the spiritual union between Isis and Osiris, who had a significant influence on the abundance of the Nile River, considered the source of life in Egypt. The vertical line in the center of the Ankh signifies the merging of opposites or the fusion of poles, within the context of concepts related to resurrection and the renewal of life.
Egyptian scholars, particularly from Cairo University, emphasize that the Ankh has substantial significance regarding the central role of the Nile River in the country. The oval head of the Ankh represents the Nile Delta, while the vertical part represents the path of the river. The horizontal section symbolizes the east and west, reflecting the ancient Egyptians’ need to protect themselves from these dimensions.

The Eye of Horus, also known as the “Eye of the Moon” or “Eye of Ra,” is an ancient Egyptian symbol with amuletic properties, used for protection against envy, evil spirits, and harm. It takes the form of a pendant worn to symbolize the royal power derived from the gods Horus and Ra. It is considered a solar symbol that embodies order and strictness. The symbol was placed on the chest of the pharaoh’s mummy to protect him in the grave. Ancient artists crafted it from gold, incorporating images of Horus, Ra, and symbols of life, permanence, and cosmic stability during the reign of the pharaohs.
In mythology, Horus is the son of King Osiris, who was killed by his uncle Seth. Horus fought violent battles to avenge his father, leading to numerous injuries, including the disfigurement of his left eye. However, thanks to the intervention of deities like Hathor or Thoth, the damaged eye was replaced with the “Udjat,” restoring his sight, as this eye possessed magical properties.
The magical amulet was first used to restore Osiris to life and became a popular charm in ancient Egypt. It was considered a symbol of strength and power, enhancing vision, healing eye diseases, protecting against envy, and helping maintain physical health and vitality. It was even associated with the ability to resurrect the dead.
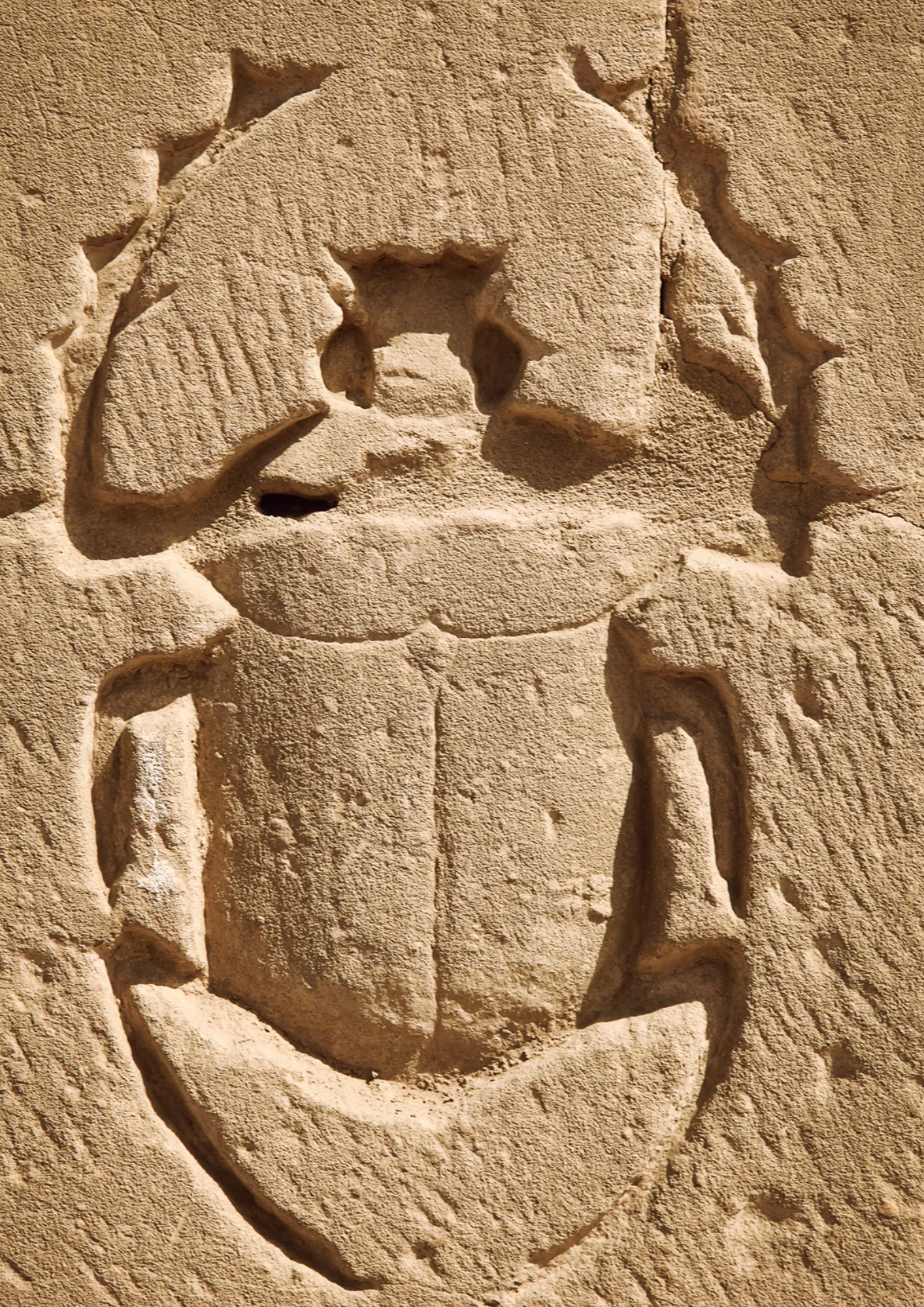

The Scarab Beetle
The scarab beetle, also known as “Apo-Phis,” is a green ceramic artifact shaped like a dung beetle, created by the ancient Egyptians for decoration. The shape was inspired by a black beetle that rolls dung to lay its eggs inside, leading the Egyptians to name it “Khepri.” Early on, the scarab was used to represent the verb “kheper,” meaning “to come into being.”
Egyptian scarabs had various uses, including serving as cylindrical seals, buttons, and large golden rings. They were also used to seal the tops of jars and letters to protect them from thieves. Egyptians believed that the scarab had protective properties, so they wore it as an amulet against evil.
The scarab was symbolically associated with the god Ra. The ancient Egyptians saw the scarab as representing the sun’s cycle, with the beetle rolling the ball of dung behind it, similar to the sun’s movement from east to west. They depicted Ra as the sun during the day and as the scarab at night, symbolizing renewal and rebirth with the sunrise.
Scarabs are prominent archaeological artifacts found in the tombs of ancient Egyptians. They are often made of “faience,” a greenish-blue ceramic material, and feature hieroglyphic inscriptions used as seals or charms. Despite the thousands found, the modern era has seen an increase in counterfeits, requiring experts to carefully examine pieces to determine their authenticity.
Scarabs vary in form, from natural shapes to representations of beetles or ram heads. They are often engraved with names, titles, and wishes reflecting Egyptian culture. Scarabs also served as historical documentation tools, containing information about kings and official roles, as well as featuring a variety of designs, protective charms, and sacred animal images. Large heart scarabs were typically made from hard stone or faience and were placed between the shrouds of the deceased, engraved with Chapter 30 from the “Book of the Dead” to ensure the heart’s safety during the weighing of the soul.
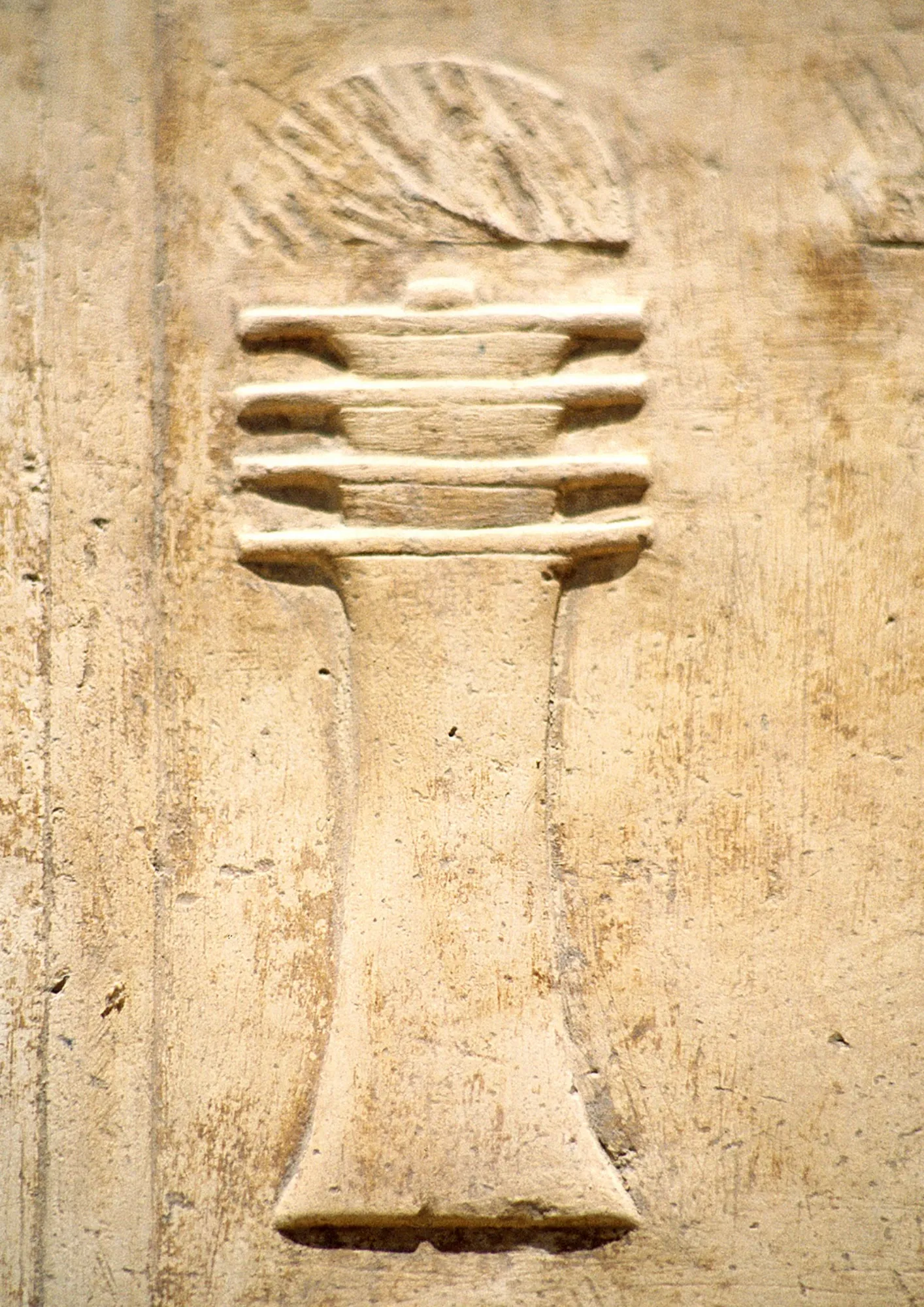

The Djed Pillar is one of the oldest Simbolos Egipcios Significados in Egyptian mythology, representing a symbol that is based on a pillar topped with four layers of lotus petals, reflecting concepts of permanence and stability. This symbol is associated with the creator god Ptah and Osiris, the god of the afterlife and the underworld, which gives the Djed Pillar a unique place in ancient Egyptian religion.
It frequently appears alongside the name of a pharaoh, often accompanied by the Ankh, symbolizing life, and the Was, symbolizing power. Together, these symbols express a wish for the pharaoh to remain a living ruler forever, reflecting the deep spiritual and political values embedded in ancient Egyptian culture.
The origins of the Djed symbol date back to prehistory in Egypt, where it was found in tombs in Helwan as a charm to protect individuals from evil. In the Old Kingdom, there were priests known as “Revered Djed,” and they celebrated the Festival of Raising the Djed Pillar, symbolizing the extension of the pharaoh’s reign.
The festival of the Djed Pillar combined the gods Ptah and Osiris, focusing on Osiris’s victory over his enemies, making Osiris celebrations more prominent. By the New Kingdom, the Djed Pillar was linked to the spine of Osiris, reflecting symbolic changes in ancient Egyptian religion.

The Lotus Flower
The name lotus comes from the Greek word “loutaz,” meaning beauty, and the lotus flower is a symbol of beauty and love. It was used in the manufacture of perfumes and cosmetics. Historically, the lotus flower symbolized the creation of the universe in ancient Egyptian culture. It is one of the most famous Simbolos Egipcios Significados.
The lotus is known as the “blue lotus” or Egyptian water lily, a water plant characterized by its beautiful shape, round leaves, and cylindrical heart. The lotus flower carries symbolic meanings associated with life, eternity, and religion.
It symbolizes the four elements of creation: its roots grow in the mud, its stems in water, its leaves in the air, and it absorbs sunlight each morning, reflecting the ancient Egyptians’ view of the interconnectedness of the universe and its components.
Famous Simbolos Egipcios Significados are an essential part of the cultural and religious heritage of ancient Egyptian civilization, carrying deep meanings and multiple connotations. These symbols illustrate the close relationship between the ancient Egyptians and their beliefs about life, death, and the gods. Famous Simbolos Egipcios Significados embody the unique understanding of the ancient Egyptian civilization regarding the world around them.
We offer tours to Egypt’s most famous destinations such as the Pyramids and Sphinx in Giza, Karnak Temple and Luxor, Valley of the Kings, Sharm El Sheikh and Hurghada for beaches and diving, and Alexandria.
We provide organized tours, luxury hotel and resort bookings, comfortable transportation services, experienced tour guides, and activity ticket bookings such as diving, desert safaris, and Nile cruises.